We all have heard the word “USB” with all its variations (such as USB 3.0, USB 3.1, or USB-C). We even use these different types of USB cables daily; we use them to charge our phone batteries, to connect gaming controllers to our console, to connect our mouse, keyboard, printer, flash drives, scammers, and more to a computer, and so on. However, we rarely ask about the differences between these models of USBs. Why are there so many different variations of USB cables and what are the differences between each of them? In this article, we will focus on answering these questions.
What is USB?
USB, which stands for Universal Serial Bus, is an industry-standard developed to make it easier for everyone to connect external devices to computers. It aims to provide defined specifications for cables, connectors, and protocols. With these specifications, consumers can effortlessly figure out which cables are appropriate for which devices. Every USB-specified cable and connector will follow a standard for connections and power supplies, and they work on any device that supports USB connections.
But acting as a connectivity standard was not the only benefit USB specifications introduced to the cable industry. The USB also increased data transfer rates, simplified software configurations, and offered plug-and-play capabilities. To this day, USB specifications have continuously improved significantly and will very likely continue to do so.

The original USB 1.0 specification was released in 1996 and could transfer data at 1.5 Mbps on low speed and 12 Mbps on full speed. At first, USB 1.0 was supposed to have a single speed of 5 Mbps, but the low speed was added to support low-cost peripherals with unshielded cables. Moreover, some devices such as keyboards, mice, and joysticks did not require high rates of transferring data, so the lower 1.5 Mbps rate of USB 1.0 could fit them well. Conversely, some other devices such as printers and floppy disk drives needed a high transfer rate of 12 Mbps transfer rate.

The USB 2.0 specification, which was released in April 2000, had a much higher data transfer rate compared to the original USB 1.0. This new specification could transfer data at 480 Mbps on High Speed, which is around 40 times more quickly than USB 1.0. It is also worth noting that both USB 2.0 and USB 1.0 are unidirectional, meaning they can either send or receive data at a given point in time.
In 2011, USB 3.0 followed USB 2.0 with significant improvements and new features. USB 3.0 benefits from SuperSpeed, supporting the transfer rate of 5 Gbps. Unlike its predecessors, this model is bidirectional; thus, it can send and receive data at the same time. Moreover, USB 3.0 can deliver up to 900mA of power, whereas USB 2.0 is only capable of up to 500mA of power.

After the release of USB 3.0, various additions such as USB 3.1 and USB 3.2 were released shortly after the original model. In 2013 USB 3.1 came out and made it possible to transfer data at the speed of 10 Gbps on SuperSpeed+. Subsequently, USB 3.2 was released in 2017, offering double the transfer rate of SuperSpeed+, making it possible to transfer data at the speed of 20 Gbps.
The most recent USB specification is USB4, which was released in 2019 and benefits from SuperSpeed+, Thunderbolt 3, and Thunderbolt 4, making it possible to transfer data at the speed of 40 Gbps, providing a speed drastically higher than its immediate predecessor and a rate that USB 1.0 and 2.0 users could have only dreamt of. USB4 uses the Thunderbolt 3 protocol specification to achieve this ultra-high speed. USB4 is also backwards compatible with USB 3.2 and USB 2.0.
Apart from the speed increases we have seen in each variation, there were other improvements and benefits as well, including decreased power consumption, increased power output, and backward compatibility. For instance, USB 3.0 can supply enough power to an external hard drive for it to no longer require an internal power supply.
So, the next time you see a term such as USB 3.0 Type-C, you will know what 3.0 stands for; it indicates the transfer rate version and speed of the USB.
But what does Type-C stand for? Let’s find out!
USB Connectors (such as USB-A and USB-C)
The next important factor you should know about the different USB connectors. There are nine main connectors: Standard A, Standard B, Standard C, Mini-A, Mini B, Mini AB, Micro-A, Micro B, and Micro AB.

USB Type-A, originally called USB Standard-A, is the first USB connector that came into existence. It is the most found USB cable and port, and we all see it very often, especially on desktop computers and large laptops. These connectors are used on many devices and quite very regularly. On the other hand, we also have USB Type-B connectors, often used for printers and many external hard drives. Standard-A cables have rectangular-shaped ports, whereas Standard B cables contain square-shaped ports.
Mini-USB and Micro-USB connectors are used for portable devices, tablets, cameras, cell phones, and some smartphones. In fact, these types of connectors were treated with warm welcomes when they found their way into the market. Companies started adopting these connectors in the mobile industry very quickly, leaving little room for other manufacturers to compete with alternative charging ports.

The latest connector is Standard C, a connector increasingly implemented in modern devices. This connector has an oval shape and is very small in size. Some of the key strengths of USB Type-C connectors, which put them above previous models, are that these connectors are faster, smaller, and can support up to 100 watts of power. So, using a Type-C cable, you can even charge laptop batteries in addition to phones and tablets. Moreover, unlike USB Type-A ports, Type-C ports are symmetrical, allowing you to connect your cable in either direction. Finally, Type-C devices support video input/output, possibly eliminating the need for video display ports such as HDMI and DisplayPort.
The Compatibilities Among USB Versions and USB Connectors
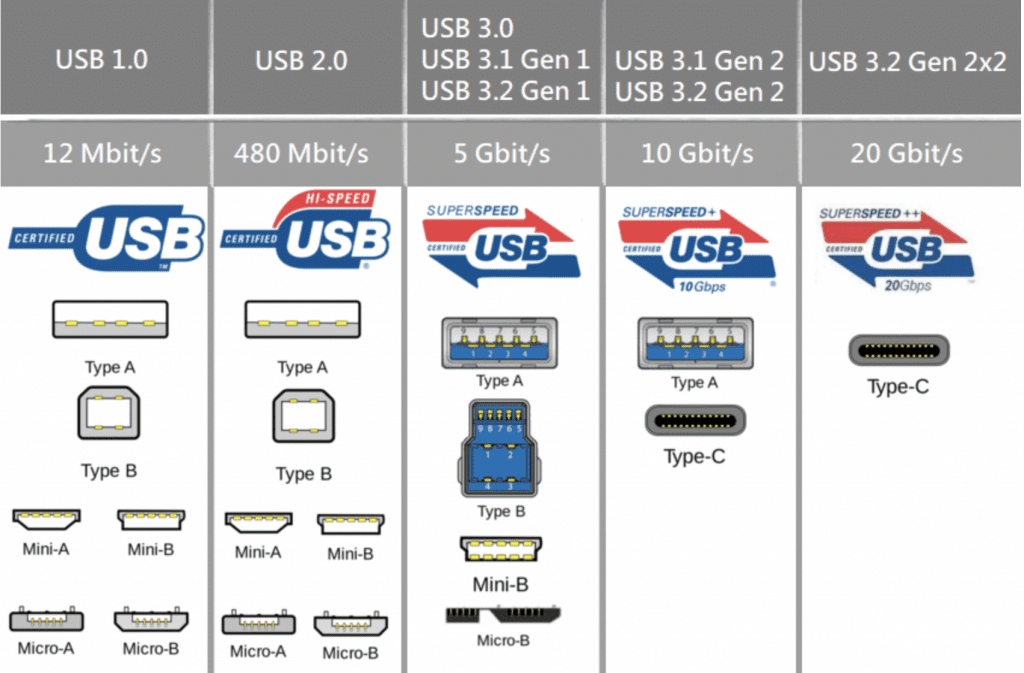
Here are all the supported connectors for each USB specification:
- USB 1.0: USB 1.0 Type-A, USB 1.0 Type-B, USB 1.0 Mini A, USB 1.0 Mini B
- USB 2.0: USB 2.0 Type-A, USB 2.0 Type-B, USB 2.0 Mini A, USB 2.0 Mini B, USB 2.0 Mini AB, USB 2.0 Micro A, USB 2.0 Micro B, USB 2.0 Micro AB
- USB 3.0: USB 3.0 Type-A, USB 3.0 Type-B, USB 3.0 Type-C, USB 3.0 Micro A, USB 3.0 Micro B, USB 3.0 Micro AB
- USB 3.1: Same as USB 3.0
- USB 3.2: USB Type-C
- USB4: USB Type-C
As you can see, since the release of USB 3.2 until this day, only Standard C has benefited from continued support from the new USB specifications. And it makes sense; the Standard C connector is small enough to fit smartphones and other handheld devices and is fast enough to charge up even slimmer laptops.
What are the factors you need to consider before purchasing a USB cable?
Now that you know some of the main aspects of various versions of USBs and their connectors, how can you purchase a USB cable that suits you the best? What are the factors you need to consider?
The most significant factor you need to consider before making any purchase is the devices’ ports you want the cable for. You should also check what ports your desired device includes and purchase a connector accordingly. For example, if your laptop does not offer any USB Type-C ports, it is a waste to purchase a USB Type-C cable simply because they offer better connectivity. Because at the end of the day, you will not be able to benefit from a USB Type-C cable on a device that does not support it.
Other factors you need to consider are the cable’s wire quality and some capabilities not dependent on the version and connector type of the USB. For instance, many cables only transfer data, whereas others can charge up a device too. Such matters are something you need to investigate before purchasing a USB cable as well.
Conclusion
USB cables and ports, with all the variations they come in, can be confusing. But once you know the basics and the fundamental features that each type provides, it becomes much easier to understand how each works and benefits you. Hopefully, this article helped you make a proper decision when purchasing a USB cable.




